Answer:
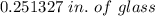
General Formulas and Concepts:
Pre-Algebra
Order of Operations: BPEMDAS
- Brackets
- Parenthesis
- Exponents
- Multiplication
- Division
- Addition
- Subtraction
Algebra I
- Terms/Coefficients
- Expand by FOIL (First Outside Inside Last)
- Factoring
Calculus
Differentiation
Derivative Notation
Basic Power Rule:
- f(x) = cxⁿ
- f’(x) = c·nxⁿ⁻¹
Integration
- Integration Property:
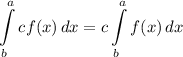
- Fundamental Theorem of Calculus:
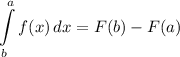
- Arc Length Formula:
![\displaystyle AL = \int\limits^a_b {√(1+ [f'(x)]^2)} \, dx](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/v17reiie6u45fk4refv7ontghpr7iciygx.png)
- Surface Area Formula:
![\displaystyle SA = 2\pi \int\limits^a_b {f(x) √(1+ [f'(x)]^2)} \, dx](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/jbbpzwal440cup9bmxrc2ttbdba7su71xw.png)
Explanation:
Step 1: Define
![\displaystyle y = (1)/(3)x^{(1)/(2)} - x^{(3)/(2)}\\Interval: [0, (1)/(3)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/14aoc28axjqyjdnv8g92oak4q6t1ssa1p9.png)
Step 2: Differentiate
- Basic Power Rule:
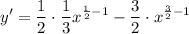
- [Derivative] Simplify:
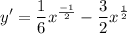
- [Derivative] Simplify:
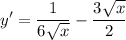
Step 3: Integrate Pt. 1
- Substitute [Surface Area]:
![\displaystyle SA = 2\pi \int\limits^{(1)/(3)}_0 {((1)/(3)x^{(1)/(2)} - x^{(3)/(2)}) \sqrt{1+ [(1)/(6√(x)) - (3√(x))/(2)}]^2}} \, dx](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/e95arnmzre0b6h0ybqv87e5zgz6qgogr2g.png)
- [Integral - √Radical] Expand/Add:
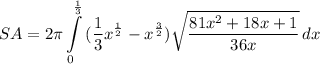
- [Integral - √Radical] Factor:
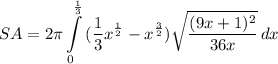
- [Integral - Simplify]:
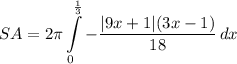
- [Integral] Integration Property:
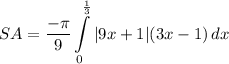
Step 4: Integrate Pt. 2
- [Integral] Define:
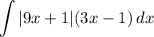
- [Integral] Assumption of Positive/Correction Factors:
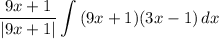
- [Integral] Expand - FOIL:
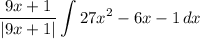
- [Integral] Integrate - Basic Power Rule:
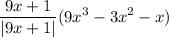
- [Expression] Multiply:
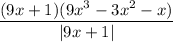
Step 5: Integrate Pt. 3
- [Integral] Substitute/Integral - FTC:
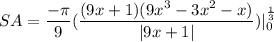
- [Integrate] Evaluate FTC:
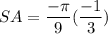
- [Expression] Multiply:
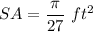
It is in ft² because it is given that our axis are in ft.
Step 6: Find Amount of Glass
Convert ft² to in² and multiply by 0.015 in (given) to find amount of glass.
- Convert ft² to in²:
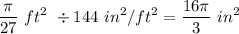
- Multiply:
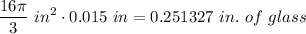
And we have our final answer! Hope this helped on your Calc BC journey!