We're minimizing the function
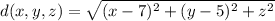
with respect to the constraint
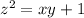
. Recall that
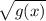
, where
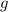
is continuous, attains its extrema at the same points as
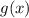
. This means we can work with
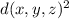
instead.
Using Lagrange multipliers: We have the Lagrangian
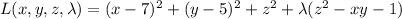
with partial derivatives
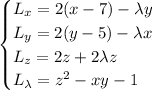
The third equation tells you that
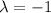
, from which you can show that
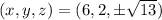
are the critical points.