Answer: Option (b) is the correct answer.
Step-by-step explanation:
Rate law is defined as the concentration of reactants and products present in the chemical reaction.
Since, in an elementary reaction the stoichiometric coefficients are equal to the order of reaction.
For example, in the given reaction
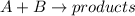 , the rate law of the reaction will be as follows.
, the rate law of the reaction will be as follows.
Here the stoichiometric coefficients are 1 for both A and B.
Thus, the rate law that correctly applies to this reaction is K[A][B].