The given question is incomplete. The complete question is:
The change in entropy is related to the change in the number of moles of gas molecules. Determine the change in moles of gas for each of the reactions and decide if the entropy increases decreases or has little to no change:
A.
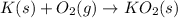
B.
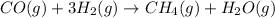
C.
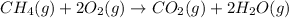
D.
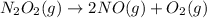
Answer: A.
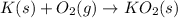 : decreases
: decreases
B.
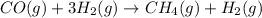 : decreases
: decreases
C.
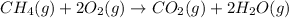 : no change
: no change
D.
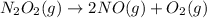 : increases
: increases
Step-by-step explanation:
Entropy is defined as the randomness of the system.
Entropy is said to increase when the randomness of the system increase, is said to decrease when the randomness of the system decrease and is said to have no change when the randomness remains same.
In reaction
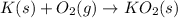 , as gaseous reactant is changed to solid product, entropy decreases.
, as gaseous reactant is changed to solid product, entropy decreases.
In reaction
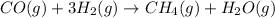 , as 4 moles of gaseous reactants is changed to 2 moles of gaseous product, entropy decreases.
, as 4 moles of gaseous reactants is changed to 2 moles of gaseous product, entropy decreases.
In reaction
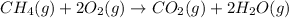 , as 3 moles of gaseous reactants is changed to 3 moles of gaseous product, entropy has no change.
, as 3 moles of gaseous reactants is changed to 3 moles of gaseous product, entropy has no change.
In reaction
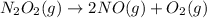 , as 1 mole of gaseous reactant is changed to 3 moles of gaseous product, entropy increases.
, as 1 mole of gaseous reactant is changed to 3 moles of gaseous product, entropy increases.