Answer:
Option C.
Step-by-step explanation:
Beta-galactosidase catalyses the hydrolysis of the sugar lactose. Lactose is a polysaccharide found in milk. Polysacharides are long-chain sugars that are made of pentose sugars (five carbon member sugars).
The enzyme is derived commercially from the E.coli bacteria and works at an optimum pH of 7 to 7.5.
A Beta-galactosidase reaction takes place in an aqueous environment (hence hydrolysis) and results in formation of and alcohol.
A typical reaction is as follows:
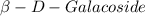
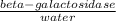 D-Galactose + Alcohol
D-Galactose + Alcohol
Hence option D