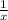Answer:
see explanation
Explanation:
Note that
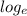 x = lnx ( natural logarithm)
x = lnx ( natural logarithm)
Using the standard derivatives
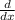 (lnx ) =
(lnx ) =
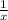 ,
,
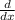 (
(
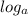 x ) =
x ) =
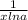
Using the chain rule
Given y = f(g(x)) , then
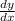 = f'(g(x))) × g'(x) ← chain rule
= f'(g(x))) × g'(x) ← chain rule
(c)
y =
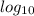 (x² - 2) then
(x² - 2) then
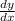 =
=
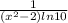 ×
×
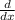 (x² - 2)
(x² - 2)
=
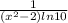 × 2x
× 2x
=
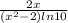
(d)
y = ln(
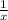 )
)
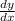 =
=
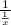 ×
×
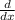 (
(
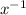 )
)
= x × -
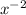
= x ×
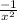
= -