ANSWER
increasing the NO concentration in the flask will shift the reaction to the left
option D
Step-by-step explanation
Given that
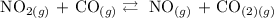
To identify the direction of the equilibrium, follow the steps below
Step 1: State Le Chatelier's principle
Le Chatelier's principle state that when an external constraint such as temperature, pressure, or concentration is imposed on a chemical equilibrium system, the equilibrium arrow will adjust so as to annul the effect of the constraint.
Looking at the reaction, you will see that the number of moles of reactants is equal to the number of moles of the products. Hence, pressure will not have effect on the reaction.
Since the reaction is a reversible reaction, the products and reactants are produced simultaneously.
Therefore, adding more of the products will favor the production of the reactants ( favors the reverse reaction)
Hence, increasing the NO concentration in the flask will shift the reaction to the left