To check for the congruency of the triangle, we will attempt to prove the Side-Side-Side (SSS) Congruence Postulate.
This we can do by finding the distance of the line segments of the triangles.
The Distance Formula is given as
![r=\sqrt[]{(x_2-x_1)^2+(y_2-y_1)^2}](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/widx51ya70zj4jlsmtdr.png)
The coordinates of the vertices are:
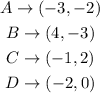
Length of AB:
![\begin{gathered} AB=\sqrt[]{(4-\lbrack-3\rbrack)^2+(-3-\lbrack-2\rbrack)^2} \\ AB=\sqrt[]{7^2+\lbrack-1\rbrack^2}=\sqrt[]{49+1} \\ AB=\sqrt[]{50} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/iaklrfvopvbjwxllibh3.png)
Length of BC:
![\begin{gathered} BC=\sqrt[]{(-1-4)^2+(2-\lbrack-3\rbrack)^2} \\ BC=\sqrt[]{\lbrack-5\rbrack^2+5^2}=\sqrt[]{25+25} \\ BC=\sqrt[]{50} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/s7k1j9h5lmfkv9mxu5ym.png)
Length of AD:
![\begin{gathered} AD=\sqrt[]{(-2-\lbrack-3\rbrack)^2+(0-\lbrack-2\rbrack)^2} \\ AD=\sqrt[]{1^2+2^2}=\sqrt[]{1+4} \\ AD=\sqrt[]{5} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/yk38csqy9iwduj65zja6.png)
Length of CD:
![\begin{gathered} CD=\sqrt[]{(-2-\lbrack-1\rbrack)^2+(0-2)^2} \\ CD=\sqrt[]{\lbrack-1\rbrack^2+\lbrack-2\rbrack^2}=\sqrt[]{1+4} \\ CD=\sqrt[]{5} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/wd9x4hlisqj040pwddc7.png)
For the SSS Congruence Postulate to apply, we must have 3 congruent sides.
From our calculations above, we have
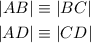
Note that |DB| is a common side in both triangles.
This proves that both triangles are congruent.