Answer:
The correct answer is:'The air particles inside the balloon move slower and push less against the sides of the balloon'.
Step-by-step explanation:
This can be explained by using Charles' Law which states that volume occupied by the gas is directly proportional to the temperature of the gas when pressure is held constant.
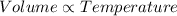 (Constant pressure)
(Constant pressure)
Kinetic energy of the gas is directly proportional to the temperature of the gas with the fall in temperature of the gas the kinetic energy of the gas will also get decreased due to which volume occupied.
Gas particles occupying less volume will now move with slower speed and and exert less pressures on the sides of the balloon.
Hence, size of the balloon decreases or shrinks when kept in freezer.