For the traits:
- Height of the sunflower, with alleles T: tall and t: short
- Color of the flower, with alleles Y: yellow and y: orange
Both traits are dominant, which means that the alleles T and Y mask the effect of the corresponding recessive alleles t and y.
To determine the phenotypic ratio of the offspring resulting of two individuals, one heterozygous for both traits (TtYy) and the other being homozygous dominant for the height but heterozygous for the flower color (TTYy), the first step is to create a punnet square with all possible allele combinations to determine the genotypes of the offspring:
Gametes of the first parent (TtYy)= TY, Ty, tY, ty
Gametes of the second parent (TTYy)= TY, Ty
Next, list the genotypes of the offspring and determine the corresponding phenotype of each individual:
Remember that the traits are dominant, which means that if the individual has only one dominant allele it will show the dominant trait.
TTYY: Tall plant and Yellow flowers
TTYy: Tall plant and Yellow flowers
TtYY: Tall plant and Yellow flowers
TtYy: Tall plant and Yellow flowers
TTYy: Tall plant and Yellow flowers
TTyy: Tall plant and Orange flowers
TtYy: Tall plant and Yellow flowers
Ttyy: Tall plant and Orange flowers
TTYY: Tall plant and Yellow flowers
TTYy: Tall plant and Yellow flowers
TtYY: Tall plant and Yellow flowers
TtYy: Tall plant and Yellow flowers
TTYy: Tall plant and Yellow flowers
TTyy: Tall plant and Orange flowers
TtYy: Tall plant and Yellow flowers
TTyy: Tall plant and Orange flowers
Count how many genotypes correspond to each phenotype:
12 Tall with yellow flowers
4 Tall with orange flowers
There is a total of 16 possible genotypes for this cross, 12 of which will present the dominant phenotypes for both traits, i.e. the plants will be Tall with yellow flowers, and 4 will present the dominant phenotype for the first trait (height) and the recessive phenotype for the second trait (flower color), i.e. the plants will be Tall with orange flowers.
To express this as a ratio you can write it as follows:
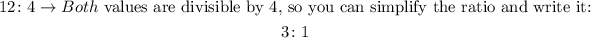
The phenotypic ratio is 3:1.
You can also express it as a percentage:
Divide the number of genotypes for each phenotype by the total number of possible combinations and multiply the result by 100:
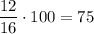
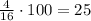
75% of the plants will have the phenotype "Tall with yellow flowers"
25% of the plants will have the phenotype "Tall with orange flowers"