Answer: The titration table for the question is given below.
Step-by-step explanation:
The equation used for the neutralization reaction is:
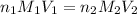
where,
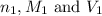 are the n-factor, molarity and volume of an acid.
are the n-factor, molarity and volume of an acid.
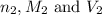 are the n-factor, molarity and volume of base.
are the n-factor, molarity and volume of base.
Molar ratio is defined as the ratio of the stoichiometric coefficients of of one reactant to the other reactant.
Concentration is the number of moles present in 1 L of solution. Molarity is unit of concentration.
The chemical equation for the reaction of potassium hydroxide and sulfuric acid is given as:
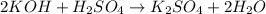
We are given:
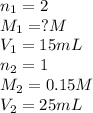
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
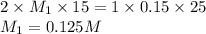
For acid, the molar ratio will be =
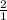
For base, the molar ratio will be =
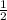
Concentration of acid
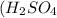 = 0.125 moles/L
= 0.125 moles/L
Concentration of base (KOH) = 0.15 moles/L
The chemical equation for the reaction of sodium hydroxide and hydrogen bromide is given as:

We are given:
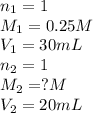
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
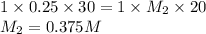
For acid, the molar ratio will be =
For base, the molar ratio will be =
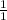
Concentration of acid (HBr) = 0.25 moles/L
Concentration of base (NaOH) = 0.375 moles/L
The table for titrations is given below.