Answer:
the work done by the net external force acting on the skier is 3046.12 J.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given;
initial speed of the water skier, u = 6.3 m/s
final speed of the water skier, v = 10.9 m/s
mass of the water skier, m = 77 kg
The work done by the net external force is calculated as;
W = ΔK.E
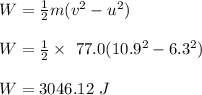
Therefore, the work done by the net external force acting on the skier is 3046.12 J.