Answer:
B.Doubling the concentration of B.
Step-by-step explanation:
Consider the rate below
![R=k[A][B]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/chemistry/high-school/8o5cx2pgic7deovn3vvr16mjfszkyi2xxn.png)
We have to find the rate of reaction is quadruple means the rate of reaction is 4 times the rate of initial rate of reaction.
Let [A}=a,[B]=b then
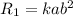
a. doubling the concentration of A
It means [A]=2a
Therefore , substituting the value
Then we get the rate of reaction
![R_2=k[2a][b]^2=2kab^2=2R_1](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/chemistry/high-school/o6qke4ylvw2pyd11w5mvi277qdlg344qf1.png)
Therefore , the rate of reaction is 2 times the initial rate of reaction.Hence, option A is false.
B.Doubling the concentration of B
It means [B]=2b
Therefore , substituting the value
Then we get the rate of reaction
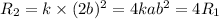
Hence, the rate of reaction is 4 times the initial rate of reaction .Therefore, the rate of reaction is quadruple.Therefore, option B is true.
C.Doubling the concentration of both A and B
[A]=2a, [B]=2b
Substitute the values then the rate of reaction
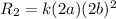
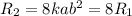
Hence, the rate of reaction is 8 times the initial rate of reaction .Therefore, it is not quadruple.Therefore, option C is false.
D.Doubling the concentration of A but halving the concentration of B
[A]=2a, [B]=
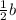
Substitute the values then the rate of reaction
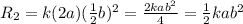
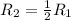
Hence, the rate of reaction is
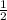 times the rate of initial rate of reaction.Therefore, option D is false.
times the rate of initial rate of reaction.Therefore, option D is false.