Answer:
i) B₃> B₁, ii) submerged body T>0, body in equilibrium or floats T=0,
iii) the same volume P₃ = P₁, different volume P₃> P₁
Step-by-step explanation:
i) The thrust force is equal to the weight of the desalted liquid
B = W = ρ g
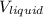
with this expression let's analyze the situation, we have two possibilities
* The two cubes have the same volume (bodies with different density) in this case The thrust on the heavier cube is greater
cube m = 3 kg B₃ = 3 9.8
B₃ = 29.4 N
cube m = 1 kg B₁ = 1 9.8
B₁ = 9.8 n
B₃> B₁
* The two cubes have different volume (same density), in this case the body with greater mass must have more volume
ρ = m / V
m = ρ V
because we have assumed that the density is the same
cube m = 3 kg B₃ = ρ g V₃
cube m = 1 kg B₁ = ρ g V₁
for this second possibility also B₃> B₁
ii) the tension in the rope that supports each cube
let's use the equilibrium condition
T + B - W = 0
T = W -B
in this case we have several possibilities, depending on whether the cube can float or sink in the liquid which changed the thrust
a) submerged body sinks in the liquid therefore the weight of the body is greater than the thrust of the liquid
T> 0
b) body in equilibrium in the liquid, in this case the thrust and weight are equal
T = 0
c) the body floats in the liquid, in this case only part of the volume of the body is submerged and this part is the one that creates a thrust (B ') less than et in equilibrium with the weight
T = W- B '
T = 0
We can see that the only case where the tension is different from zero is when the body sinks, for this possibility, as the thrust of the heavier body is greater
cube m = 3kg T₃ = W₃ -B₃
cube m = 1 kg T₁ = W₁ - B₁
For this case, the density of the body must be known to calculate especially the thrust in each case, if the two bodies have the same density
T₃> T₁
iii) The pressure on the lower part of the cube, there are several cases
* The two cubes with the same volume, in this case the height of the cubes is the same
P = ρ g h
the pressure for both cubes is the same
P₃ = P₁
* the two have different volume, we assume that h₃> h₁
therefore P₃> P₁