Answer:
see explanation
Explanation:
Using the chain rule and the standard derivatives
Given
y = f(g(x)) , then
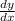 = f'(g(x)) × g'(x) ← chain rule
= f'(g(x)) × g'(x) ← chain rule
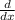 (tanx) = sec²x ,
(tanx) = sec²x ,
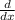 (cotx) = - csc²x
(cotx) = - csc²x
(c)
y = tan
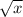 = tan
= tan
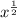
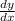 = sec²
= sec²
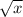 ×
×
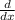 (
(
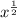 )
)
= sec²
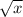 ×
×
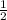
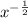
= sec²
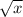 ×
×
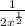
=
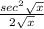
(d)
y = cot(1 + x)
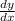 = - csc²(1 + x) ×
= - csc²(1 + x) ×
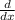 (1 + x)
(1 + x)
= - csc²(1 + x) × 1
= - csc²(1 + x)