Answer:
The molar solubility is
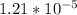
Step-by-step explanation:
In others words, a compound's molar solubility tells us how many moles of a compound can be dissolved in exactly one liter of water in order to make a saturated aqueous solution (solution that has a balance between solvent and solute at the given temperature).
A solute formed by ions, as in this case, the following equilibrium is established:
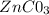 ⇒
⇒
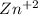 +
+
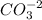
You can see that 1 mole of
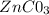 produces 1 mole of zinc cations and 1 mole of carbonate anions.
produces 1 mole of zinc cations and 1 mole of carbonate anions.
The equilibrium of solubility is the relationship between the solid and dissolved states of a saturation compound.
For the ionic compounds a solubility constant is used, which we call Kps. The kps is the result of the multiplication of the concentration of ions involved. In this case:
![Kps=[Zn^(+2) ]*[CO_(3) ^(-2) ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/chemistry/high-school/wismgdwtnj8my2eked7qzvhs85n4cz2iyu.png)
The zinc carbonate salt
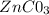 is insoluble in water. This means that you can consider "s" as the molar concentration of zinc cations dissolved in equilibrium and the molar concentration of carbonate anions. They are the same because, being the insoluble salt, they are produced in equal quantities when the salt dissociates.
is insoluble in water. This means that you can consider "s" as the molar concentration of zinc cations dissolved in equilibrium and the molar concentration of carbonate anions. They are the same because, being the insoluble salt, they are produced in equal quantities when the salt dissociates.
![[Zn^(+2) ]=[CO_(3) ^(-2) ]=s](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/chemistry/high-school/5cfg5ge0znrnbb8penq6xkp55p3goqha2l.png)
So, you have
Kps=s*s
Kps=s²
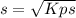
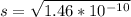
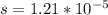
Remember that "s" is the molar concentration of dissolved ions. In this case, since the salt is insoluble as mentioned above, "s" will also be the molar solubility of the salt, this is how many moles of the solid dissociate to produce moles of dissolved ions.
So you can say that you can dissolve
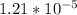 moles of solid zinc carbonate in 1 L of water
moles of solid zinc carbonate in 1 L of water