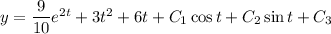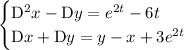
Adding the two ODEs gives
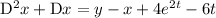
Differentiating once gives
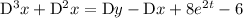
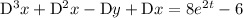
The first ODE lets you simplify this a bit:
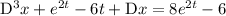
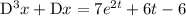
Let
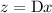
, so that
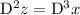
, and reduce the order of the ODE to get
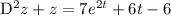
Solving this ODE for

shouldn't be a problem for you; you would find that
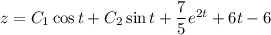
Since
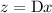
, integrating once with respect to
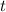
gives the general solution for

:
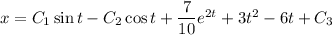
Now plug in the second derivative of this solution into the first ODE to find another ODE in
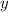
alone.
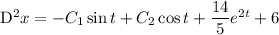
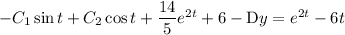
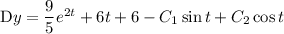
Integrate with respect to
and you get