The calorimeter is an equipment that allows to measure the heat released or absorbed during a chemical reaction.
To make the calculations we are going to assume that there are no heat losses to the environment and that all the heat released by the chemical reaction is absorbed by the water.
I say that it is absorbed by the water because we are told for both reactions that the water increases its temperature. This is an indication that the reaction is exothermic, that is to say that the reaction releases heat and this heat is absorbed by the water causing the temperature to increase.
So for the first answer, it will be Exothermic.
Now, to calculate the heat released by the reaction we will apply the following equation:
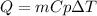
Where,
Q is the absorbed heat by the water
Cp is the specific heat of water, 4.186kJ/g°C
m is the mass of water. 1400g
dT is the difference of temperature. Final temperature-Initial temperature
So, the heat absorbed by the water will be:
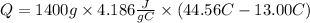
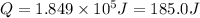
The heat absorbed by the water will be greater than the heat released by the reaction. So, the second answer will be 185.0kJ
Now, to find the heat per mole of ethane, we must divide the total heat released by the number of moles of ethane. The moles of ethane will be equal to the grams of ethane divided by its molar mass.
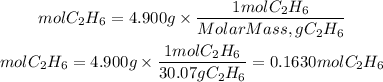
So, the heat released by mol of ethane will be:
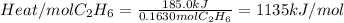
The third answer will be: 1135kJ/mol