Answer: 1. gain of electrons: reduction
2.low
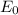 : weak oxidiser
: weak oxidiser
3. loss of electrons: oxidation
4. high
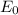 : strong oxidiser
: strong oxidiser
5. negative ions: anions
6. positive ions: cations
7. migrate to cathode : positive ions
8. migrate to anode : negative ions
Explanation: Reduction is the process in which electrons are gained and thus there is decrease in the oxidation number.
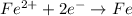
Oxidation is the process in which electrons are lost and thus there is an increase in the oxidation number.
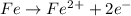
Elements with high reduction electrode potentials
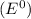 can easily accept electrons and thus themselves get reduced and thus act as good oxidizing agents.
can easily accept electrons and thus themselves get reduced and thus act as good oxidizing agents.
Elements with low reduction electrode potentials
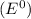 can easily lose electrons and thus themselves get oxidized and thus act as good reducing agents.
can easily lose electrons and thus themselves get oxidized and thus act as good reducing agents.
The anions bearing negative charge are called as anions and the ions bearing positive charge are called as cations.
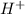 is action and
is action and
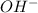 is an anion.
is an anion.
In electrolytic cell, Cathode is a negatively charged electrode and thus attracts cations bearing positive charge and anode is a positively charged electrode and thus attracts anions bearing negative charge.