Answer:
Underwater
Step-by-step explanation:
One of the most important difference between Earth and Mars is the strength of gravity at the surface. In fact, at the Earth's surface, the strength of the gravitational field is
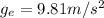
Instead, on Mars' surface is only
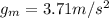
So, much lower than Earth.
In order to test the lander properly, it must be tested in an environment where gravity is lower than its normal value on Earth. This can be done by testing the lander underwater. In fact, when an object is underwater, it experiences an upward force (called buoyancy). The effect of this force is to decrease the "apparent gravity" on the object: in fact, net force on the object is equal to its weight:
F = mg (downward)
So the acceleration is g. However, due to the presence of the buoyancy, the net force on the object is
F = mg - B
So the apparent gravity on the object will be
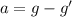
And therefore, this "trick" allows to test the lander in an environment with lower gravity, so more similar to Mars surface.