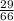Answer:
23 29/66
Explanation:
If Malik and Erin harvest about 2 1/3 acres' worth of corn each day and they have 10 1/22 days to harvest the field, the total acres that can be harvested would be the product of 2 1/3 and 10 1/22
2
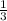 x 10
x 10
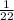
Convert the mixed fractions to an improper fraction
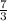 x
x
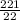 =
=
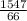
Convert the improper fraction back to mixed fraction To do this, divide the numerator by the denominator, the number got would be the whole number of the mixed fraction. The remainder would be the numerator
23