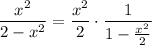
Since
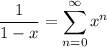
for
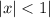
, the power series for the rightmost rational expression is
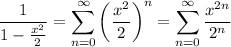
which is applicable for
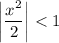
, or

.
Distributing the other rational expression gives
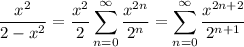
I'm not sure what is meant by "simplify the summation to a single variable", but you can rewrite this as
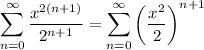
which could be interpreted as a simpler form, but that's really in the eye of the beholder...