1. What is the initial velocity of the tennis ball at the moment of its release at the top of the track? Use this insight to calculate the initial and potential kinetic energy.
Answer:
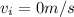
Step-by-step explanation:
As initially it starts from hill A so its initial KE = 0 so initial speed is also zero
Also its initial potential energy is given as
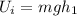
here we know
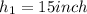
2. Calculate the amount of gravitational potential energy at the top of each hill and at the bottom of each valley. Be sure to convert your distance measurements to meters. Use and approximate value of 58.0 g. for the mass of the tennis ball, and 9.81 m/s squared as the acceleration due to gravity.
Answer:
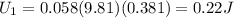
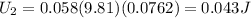
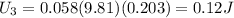
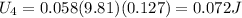
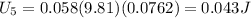
Step-by-step explanation:
As we know that gravitational potential energy is given as
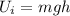
here we know for hill A
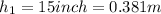
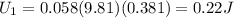
For Valley B
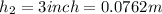
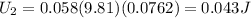
For Hill C
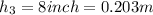
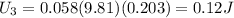
For valley D
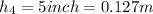
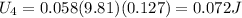
For Hill E
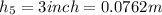
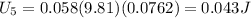
3. Suppose that the force due to friction is negligible. What can you say about the total energy of the tennis ball? Continue to assume that the force due to friction is negligible. Use the information you've gathered to calculate the kinetic energy and the total energy at each location. Describe the relationship between the potential and kinetic energy of the tennis ball as it travels the length of the roller coaster.
Answer:
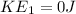
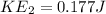
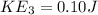
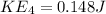
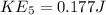
Step-by-step explanation:
Total energy will remain conserved in all cases as friction is not here
so here we will say
Total energy is 0.22 J
now kinetic energy as Hill A
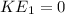
kinetic energy at Valley B
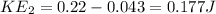
kinetic energy at Hill C

Kinetic energy At Valley D
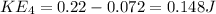
Kinetic energy at Hill E
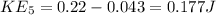
4. Compare your answer to the previous question with your observations In conducting this experiment. Discuss weather energy was conserved in your experiment. Was friction negligible?
ANSWER
In actual experiment if the friction force is negligible then in that case the final kinetic energy at each case is nearly same but if the friction is not negligible then in that case the final kinetic energy will not be same as we calculated above due to energy loss in friction.