The given is a discrete random variable.
For a discrete random variable, the expected value is calculated by summing the product of the value of the random variable and its associated probability, taken over all of the values of the random variable.
It is given that the probability of a flood is 1%=0.01.
It follows that the probability of no flood is (100-1)%=99%.
Hence, the expected net gain is:
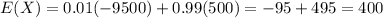
Hence, the expected net gain is $400.
The expected net gain is E(X) = $400.