Answer:
T=240.56 °K
Step-by-step explanation:
Ideal gases are a simplification of real gases that is done to study them more easily. It is considered to be formed by point particles, do not interact with each other and move randomly. It is also considered that the molecules of an ideal gas, in themselves, do not occupy any volume.
The pressure, P, the temperature, T, and the volume, V, of an ideal gas, are related by a simple formula called the ideal gas law:
P*V = n*R*T
where P is the gas pressure, V is the volume that occupies, T is its temperature, R is the ideal gas constant, and n is the number of moles of the gas. The universal constant of ideal gases R has the same value for all gaseous substances. The numerical value of R will depend on the units in which the other properties are worked.
Now, taking into account this law, and isolating the temperature variable (T), you get:
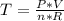
Taking into account the data values and replacing in the previous equation, you get:
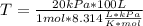
Remember to check the units, but in this case you can see that it is not necessary to convert them.
Then, the temperature in the given conditions will be:
T=240.56 °K