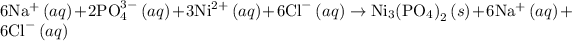The complete ionic equation for reaction 1 is as follows:
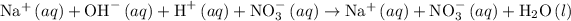
The net ionic equation for reaction 2 is as follows:
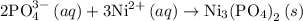
The complete ionic equation for the reaction 3 is as follows:
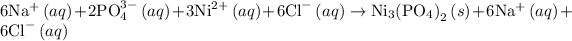
Further Explanation:
The three types of equations that are used to represent the chemical reaction are as follows:
1. Molecular equation
2. Total ionic equation
3. Net ionic equation
The reactants and products remain in undissociated form in molecular equation. In the case of total ionic equation or complete ionic equation, all the ions that are dissociated and present in the reaction mixture are represented while in the case of net or overall ionic equation only the useful ions that participate in the reaction are represented.
A) Steps to write the complete ionic equation of reaction 1 is as follows:
Step 1: Write the molecular equation for the reaction with the phases in the bracket.
In the reaction,
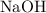 reacts with
reacts with
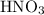 to form
to form
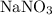 and
and
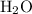 . The balanced molecular equation of the reaction is as follows:
. The balanced molecular equation of the reaction is as follows:
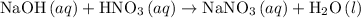
Step 2: Dissociate all the compounds with the aqueous phase to write the total ionic equation. The compounds with solid and liquid phase remain same.
The complete ionic equation for reaction 1 is as follows:
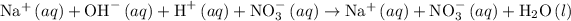
B) Steps to write the net ionic equation for the reaction 2 is as follows:
Step 1: Write the molecular equation for the reaction with the phases in the bracket.
In the reaction,
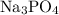 reacts with
reacts with
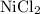 to form
to form
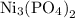 and
and
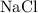 . The balanced molecular equation of the reaction is as follows:
. The balanced molecular equation of the reaction is as follows:
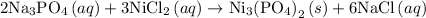
Step 2: Dissociate all the compounds with the aqueous phase to write the total ionic equation. The compounds with solid and liquid phase remain same.
The complete ionic equation for the reaction 2 is as follows:
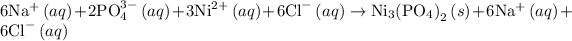
Step 3: The common ions on both the sides of the reaction get cancelled out to get the net ionic equation.
The net ionic equation for reaction 2 is as follows:
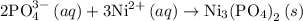
C) Steps to write the complete ionic equation for the reaction 3 is as follows:
The reaction 3 is same as the reaction 2 and therefore the complete ionic equation for the reaction 3 is as follows: