Step-by-step explanation:
It is given that,
Mass of the child, m = 30 kg
It sits at a height, h = 3 m
Speed of child, v = 4 m/s
1. The potential energy at the start is given by :
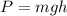
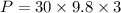
P = 882 J
2. Kinetic energy at the end is given by :
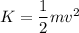
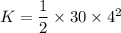
K = 240 J
3. Energy lost due to friction,
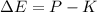
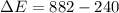
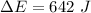
Hence, this is the required solution.