Answer:
v = 14.5 m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
The Principle Of Conservation Of Mechanical Energy
In the absence of friction, the total mechanical energy is conserved. That means that
Em=U+K is constant, being U the potential energy and K the kinetic energy
U=mgh
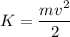
The ball with a mass of m=0.8 kg is thrown straight upward from the zero height reference (h=0) and with some speed (v). The potential energy is zero, but the kinetic speed is given by the equation above.
When the ball reaches its maximum height of h=10.7 m, the speed is zero and all the initial kinetic energy was transformed into potential energy, thus:
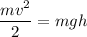
Simplifying by m:
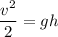
Solving for v:
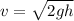
Substituting:

Calculating:
v = 14.5 m/s