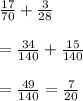Even with fractions, we still use the order of operations. The acronym to remember this is PEMDAS. First is parentheses, then exponents, multiplication/division, addition/subtraction.
The given problem is

.
First we simplify what's in the parentheses. PEMDAS then applies in the parentheses, and since they are no further parentheses or exponents, we look at multiplication/division and multiply. First let's have all improper fractions.
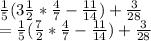
.
Next multiply the fractions: numerator with numerator and denominator with denominator.
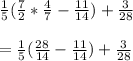
Next in the parentheses is addition/subtraction.
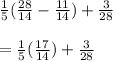
Now apply PEMDAS again, and since there are no parentheses or exponents to simplify, we multiply.
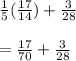
Finally find a common denominator and add.