Answer:
Explanation:
Given: i. AB||DE
ii. AC≅DC
Prove: ΔABC≅ΔDEC
From the two triangles, it can be observed that;
m<BAC≅m<EDC (alternate angles)
m<ABC≅m<DEC (alternate angles)
m<BCA≅m<ECD (vertically opposite angles)
m<BAC + m<ABC + m<BCA = m<EDC + m<DEC + m<ECD =
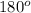 (sum of angles in a triangle)
(sum of angles in a triangle)
Since the three angles of the triangles are congruent respectively, then;
ΔABC≅ΔDEC (AAA congruence property)