Answer:
128 grams of oxygen, O₂, is required for the complete combustion of 36 grams of pentane, C₅H₁₂ under standard conditions.
Step-by-step explanation:
The balanced reaction is:
C₅H₁₂ + 8 O₂ ⇒ 5 CO₂ + 6 H₂O
By stoichiometry of the reaction (that is, the relationship between the amount of reagents and products in a chemical reaction), the following amounts of each compound participate in the reaction:
- C₅H₁₂: 1 mole
- O₂: 8 moles
- CO₂: 5 moles
- H₂O: 6 moles
Being the molar masses of the compounds:
- C₅H₁₂: 72 g/mole
- O₂: 32 g/mole
- CO₂: 44 g/mole
- H₂O: 18 g/mole
then, by stoichiometry, the following quantities of mass participate in the reaction:
- C₅H₁₂: 1 mole* 72 g/mole= 72 g
- O₂: 8 moles* 32 g/mole= 256 g
- CO₂: 5 moles* 44 g/mole= 220 g
- H₂O: 6 moles* 18 g/mole= 108 g
Then you can apply the following rule of three: if by stoichiometry 72 grams of pentane react with 256 grams of oxygen, then 36 grams of pentane with how much mass of oxygen does it react?
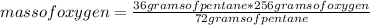
mass of oxygen= 128 grams
128 grams of oxygen, O₂, is required for the complete combustion of 36 grams of pentane, C₅H₁₂ under standard conditions.