Answer: The limiting reagent for the given chemical reaction is hydrogen.
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the number of moles, we use the equation:
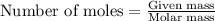 .....(1)
.....(1)
Given mass of nitrogen = 49.84 g
Molar mass of nitrogen = 28 g/mol
Putting values in above equation, we get:
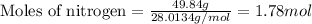
Given mass of hydrogen = 10.7 g
Molar mass of hydrogen = 2 g/mol
Putting values in above equation, we get:
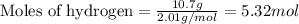
For the given chemical reaction:
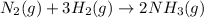
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
3 moles of hydrogen reacts with 1 mole of nitrogen.
So, 5.32 moles of hydrogen reacts with =
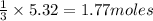 of nitrogen.
of nitrogen.
As, the given amount of nitrogen is more than the required amount, so it is considered as an excess reagent.
Thus, hydrogen is considered as an limiting reagent because it limits the formation of products.
Hence, the limiting reagent for the given chemical reaction is hydrogen.