ANSWER:
Explanation:
The first thing is to convert the time into a second, just like this:
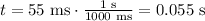
Now, convert the angular displacement of the eyelid from degrees to rad:
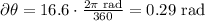
We can calculate the angular velocity, dividing the angular momentum by the time, like this:
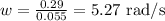
The angular acceleration is calculated by means of the quotient of the difference in angular velocity and time, like this:
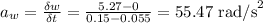
the tangential acceleration would be: