The question requires us to calculate the mass of reactant (O2) necessary to obtain 15 L of the product (NO2) under the conditions given.
The following information was provided by the question:
- Balanced chemical reaction: 2 NO(g) + O2(g) → 2 NO2(g)
- Final volume of NO2: 15 L
- Pressure: P = 752 mmHg
- Temperature: 344 K
- Gas constant: R = 0.08206 L⋅atm/mol⋅K
To solve this question, we'll need to go through the following steps:
1) calculate the number of moles that corresponds to 15 L of NO2, considering the temperature and pressure given;
2) use the stoichiometric relation to calculate the necessary amount of O2 to produce the previously calculated number of moles of NO2
3) use the molar mass of O2 and the value calculated on step 2 to obtain the necessary mass of O2
Next, we'll solve the problem following these steps:
1) To calculate the number of moles of NO2, we'll use the following equation:
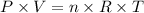
where P is the pressure, V is the volume of gas, n is the number of moles, R is the constant of gases and T is the temperature.
If we rearrange the equation to calculate the number of moles, we'll have:
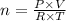
Note that the problem provided all necessary information for this calculation, but the pressure given (752 mmHg) needs to be converted into atm to match the constant provided.
To do that, we'll use the following:
1 atm = 760 mmHg
Thus, we need to divide the value provided by 760:
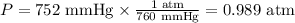
Now, we can apply the values of pressure, volume and temperature, as well as the constant provided, to the equation written above:
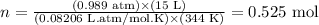
So far, we have that the volume of NO2 to be produced (15 L) corresponds to 0.525 mol under the conditions of pressure and temperature provided.
2) Next, we use the chemical reaction to calculate the number of moles of O2 required to produce 0.525 mol of NO2.
From the reaction, we have that 1 mol of O2 leads to 2 mol of NO2. Then, we use this to calculate how many moles of O2 would produce 0.525 moles of NO2:
1 mol O2 --------------- 2 mol NO2
x -------------------------- 0.525 mol NO2
Solving for x, we have:
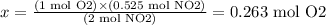
Now, we know that 0.263 moles of O2 are necessary to produce 15 L of NO2
3) The last step is calculate the mass of O2 that corresponds to 0.263 moles of this compound.
To do this, we need the molar mass of O2. Since the atomic mass of oxygen is 15.99 u, the molar mass of O2 is:
molar mass O2 = (2 * 15.99) = 31.98 g/mol
With this information, we can calculate the mass of 0.263 moles of O2:
1 mol O2 -------------------- 31.98 g O2
0.263 mol O2 ------------ y
Solving for y, we have:
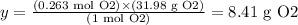
Therefore, the mass of O2 necessary to produce 15 L of NO2 under the conditions given is 8.41 g.