It's similar to how you might solve an inequality involving a polynomial. For example,
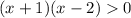
First consider the case when the left side actually is zero. This happens when
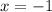
and
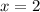
. Pick numbers that fall to either side of these values and plug them into the inequality.
For instance, take

(to the left of -1),
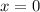
(between -1 and 2), and
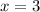
(to the right of 2). You have

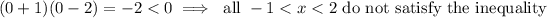
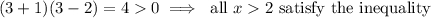
So the polynomial is positive for
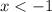
and
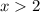
.
You can use a similar analysis to determine the sign of the second derivative over certain intervals.