Answer:
0.1498 g of O2.
Step-by-step explanation:
The Behavior of Gases => Ideal Gas Law.
The ideal gas law is a single equation that relates the pressure, volume, temperature, and the number of moles of an ideal gas, which is:
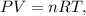
where P is pressure in atm, V is the volume in liters, n is the number of moles, R is the ideal gas constant (0.082 L*atm/mol*K), and T is the temperature in the Kelvin scale.
So we have to convert pressure from 700.0 mmHg to atm, volume from 120.0 mL to L, and 15 °C to K.
Let's convert pressure taking into account that 1 atm equals 760 mmHg, like this:
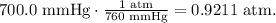
Remember that 1 L equals 1000 mL, so 120.0 mL would be equal:
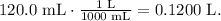
And the conversion from °C to K is just sum °C with 273, so 15 °C in K is:
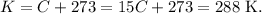
Finally, we can use the ideal gas formula, solving for 'n' (number of moles) and replacing the data that we have, as follows:

Now, the final step is to convert 4.680 x 10⁻³ moles of O2 to grams using the molar mass of O2 that can be calculated using the periodic table, which is 32 g/mol. The conversion will look like this:
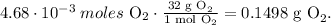
The answer would be that there are 0.1498 g of O2.