Answer: 48,501 J/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
1) Action barrier = activation energy = Ea
2) Data:
i) T₁ = 12°C = 12 + 273.15 K = 285.15K
ii) T₂ = 22°C = 22 + 273.15 K = 295.15 K
iii) rate constant = k: k₂ / k₁ = 2
iv) Ea = ?
3) Formula:
Arrhenius' law gives the relationship between the constant of reaction and the temperature:
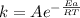
4) Solution
By arranging the formula, you get:
㏑[k₂/k₁] =Ea/R [1/T₁ - 1/T₂]
Replace k₂ = 2k₁; T₁ = 285.15; and T₂ = 295.15
ln[2] = Ea/8.314 J/K mol × [1/285.15 - 1/295.15]K
Ea = ln [2] × 8.314 J/K mol / [1.18818×10⁻⁴K] = 48,501 J/mol