Answer:
The equilibrium constant of reaction at given temperature is 0.28.
Step-by-step explanation:
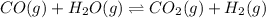
Initially
0.35 mol 0.40 mol
At equilibrium
(0.35 mol-x) (0.40 mol-x) x x
Moles of CO left at equilibrium = 0.22 mol
0.22 mol = (0.35 mol-x)
x = 0.35 mol - 0.22 mol = 0.13 mol
Moles of
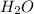 left at equilibrium = 0.40 mol - 0.13 mol = 0.27 mol
left at equilibrium = 0.40 mol - 0.13 mol = 0.27 mol
Concentration of CO at equilibrium =
![[CO]=(0.22 mol)/(1 L)](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/chemistry/high-school/qx33ry5dadxr3i8dnvzkwi1r1ub3o5ulb7.png)
Concentration of
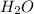 at equilibrium =
at equilibrium =
![[H_2O]=(0.27 mol)/(1 L)](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/chemistry/high-school/kyqaxrt12n8oogbiyxzxaoksyg7vum76sg.png)
Concentration of
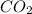 at equilibrium =
at equilibrium =
![[CO_2]=(0.13 mol)/(1 L)](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/chemistry/high-school/6brruogm6o7m76l9dfj9xpkjixqlzmib7e.png)
Concentration of
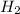 at equilibrium =
at equilibrium =
![[H_2]=(0.13 mol)/(1 L)](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/chemistry/high-school/l9571dff2v9f7hs7ikh84wl3dmc34z8y5o.png)
![K=([CO_2][H_2])/([CO][H_2])](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/chemistry/high-school/xfdyusywqaq70tem0pc90hficfz51wp0ol.png)
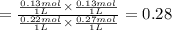
The equilibrium constant of reaction at given temperature is 0.28.