Partitioning the interval
![[6,11]](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/mathematics/high-school/cgvadqz8b06nzx6w8qgzq5np5a3j7tb242.png)
into
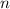
equally-spaced subintervals gives
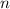
rectangles of width

and of heights determined by the right endpoints of each subinterval.
If

, then

,

, and so on, up to

. Because we're using the right endpoints, the approximation will consider

The definite integral is then approximated by

You have




To check that this is correct, let's make sure the sum converges to the exact value of the definite integral. As
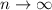
, you have the sum converging to

.
Meanwhile,
![\int_6^(11)(1-5x)\,\mathrm dx=\left[x-\frac52x^2\right]_(x=6)^(x=11)=-\frac{415}2](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/mathematics/high-school/botw58sm7cla4f9ddfk5fmgxo29vrtwelu.png)
so we're done.