Answer 1 : The correct option is, move faster
Explanation :
As we know that the kinetic energy of the particle of the gas is directly proportional to the temperature of the gas. That means higher the temperature higher will be the kinetic energy.
When the Kelvin temperature of an enclosed gas doubles, the kinetic energy will be double and then the particles of the gas move faster.
Answer 2 : The correct option is, It increases by a factor of eight.
Explanation :
According to the Boyle's law, the volume of the gas is inversely proportional to the pressure of the gas at constant temperature and the number of moles of gas.
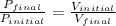
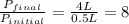
Hence, the gas pressure change increases by a factor of eight.
Answer 3 : The correct option is, the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature in kelvins.
According to the Charles's law, the volume of the gas is directly proportional to the temperature of the gas at constant pressure and the number of moles of gas.
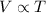
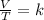
Answer 4 : The correct option is, 36 ml
Solution : Given,
initial volume = 17 ml
initial temperature =
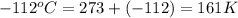
final temperature =
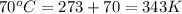
Formula used :
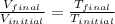
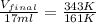
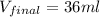
Therefore, the volume of the sample occupy at
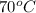 is, 36 ml
is, 36 ml
Answer 5 : The correct option is, temperature, pressure, and volume
Explanation :
Combined gas law is the combination of the Boyle's law, Charles's law and Gay Lussac's law at constant number of moles of gas.
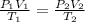
The variable used in the combined gas law are temperature, pressure, and volume .