First you need to calculate the velocity of the stone when it reaches the ground level. This is easy to find from energy conservation, since the potential energy it had at the top of the tower has been totally converted into kinetic energy.
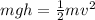
We don't know the mass of the stone, but it cancels from both equations. This gives
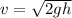
so v=44.27 m/s.
Now, the time it took the stone to fall from the top of the tower to the ground is calculated easily from
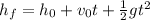
.
The initial velocity is 0, the initial height is 100 meters and the final height is 0 since we are taking the ground floor as height 0.
This gives
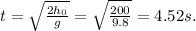
So the time it took the stone to fall from the ground level to the bottom of the well is 5-4.52=0.48 s.
We can now use
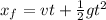
where v is the velocity we calculated before v=44.27 m/s, time is t=0.48 s and xf is the depth of the well.
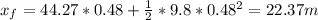
So the solution is 22.5 m