Answer: Option (D) is the correct answer.
Step-by-step explanation:
According to Le Chatelier's principle, any disturbance caused in an equilibrium reaction will tend to shift the equilibrium in a direction away from the disturbance.
So, any change in concentration, pressure, catalyst etc will not lead to any change in equilibrium constant.
But when we increase temperature then equilibrium will shift in a direction where temperature is reduced again.
For example,
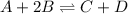
![K_(eq) = ([C][D])/([A][B]^(2))](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/chemistry/high-school/g5esipgc07ft9u55s1wnvehgi8bf4lvzvm.png)
So, when we increase the temperature in forward direction then equilibrium will shift in the backward direction leading to more of A and B and less of C and D.
Thus, we can conclude that increasing temperature stressors will affect the value for
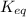 according to Le Chatelier's principle.
according to Le Chatelier's principle.