Explanation :
It is given that
mass of ball A
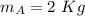
mass of ball B,
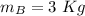
initial velocity of ball A,
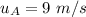 (in right)
(in right)
initial velocity of ball B,
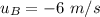 (in left)
(in left)
final velocity of ball A,
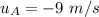 (in left)
(in left)
final velocity of ball B,
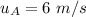 (in right)
(in right)
(1) After collision the velocities of balls gets exchanged.The velocity of ball A and B will become 9 m/s and 6 m/s but in opposite direction.
This represents Newton's third law.
(2) Initial momentum,
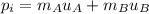
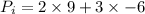
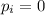
Final momentum,
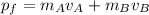
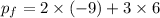
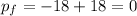
So, this shows momentum is conserved.
(3) If masses and initial velocities of each ball were same, then
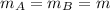 and
and
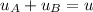
So,
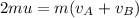
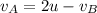
and
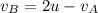
This is required solution.