Answer:
a) F_{net } = 5 i ^ N , b) F_{net } = 5 N, θ = 0
Step-by-step explanation:
Force is a vector magnitude, one of the easiest methods to work with it is to use its Cartesian components and perform the sum on each axis in scalar form.
Therefore we will create a coordinate system and sum on each axis
X axis
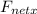 = F₁ + F₂
= F₁ + F₂
where they indicate the value of each one
F₁ = 15 N i ^
F₂ = -10 N i ^
where on the x-axis the direction to the right is positive
F_{net x} = 15 - 10
F_{net x} = 5 N
Y Axis
F_{net y} = F₃ + F₄
the values of this force are given and the upward direction is taken as positive
F₃ = 20 N j ^
F₄ = -20 N j ^
we calculate
F_{net y} = 20 -20
F_{net x} = 0
we can give the result in two ways
a) F_{net } = 5 i ^ N
b) in the form of module and angle.
Let's use the Pythagorean theorem
F_{net }² = F_{net x}² + F_{net y}²
F_{net }² = 5² + 0²
F_{net } = 5 N
we use trigonometry for the angles
tan θ = F_{net yy} / F_{net y}
θ = tan⁻¹ (0/5)
θ = 0