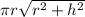Answer:
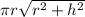
Explanation:
Given that there is a cone with radius r and slant height s.
We know that lateral surface area of the cone is
=
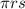
Alternately if instead of s, h is known we can write this in terms of h also.
Consider the right triangle formed by slant height, height and radius of the cone.
Using Pythagorean theorem we have
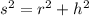
Or
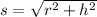
Hence lateral surface area of the cone
=