Step-by-step explanation:
Molarity is the number of moles present in a liter of solution.
Mathematically, Molarity =
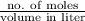
And, no. of moles =
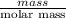
Molar mass of
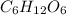 is 180.15 g/mol. Therefore, number of moles present will be as follows.
is 180.15 g/mol. Therefore, number of moles present will be as follows.
No. of moles =
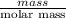 =
=
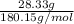
= 0.157 mol
Hence, calculate the molarity as follows.
Molarity =
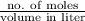
=
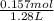
= 0.122 M
Thus, we can conclude that molarity of the solution is 0.122 M.