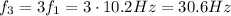(a) The lowest frequency (called fundamental frequency) of a wire stretched under a tension T is given by
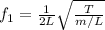
where
L is the wire length
T is the tension
m is the wire mass
In our problem, L=10.9 m, m=55.8 g=0.0558 kg and T=253 N, therefore the fundamental frequency of the wire is
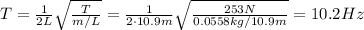
b) The frequency of the nth-harmonic for a standing wave in a wire is given by
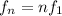
where n is the order of the harmonic and f1 is the fundamental frequency. If we use n=2, we find the second lowest frequency of the wire:
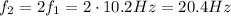
c) Similarly, the third lowest frequency (third harmonic) is given by