→ Answer:
2.48 L
→ Explanation:
Equation: CH₄(g) + 2O₂(g) → CO₂(g) + 2H₂O(g)
Table of given conditions:
![\left[\begin{array}{cccc}&Volume(L)&Pressure(atm)&Temperature(K)\\Methane&2.8&1.65&298\\Oxygen&35&1.25&304\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/v1j72667m2gh5ht81n26pszskwz36r52pf.png)
note: K = C° + 273 (Temperature conversion, Celsius to Kelvin)
Find moles of methane and oxygen:
note:
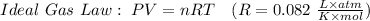
Formula to find moles is:
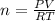
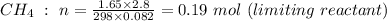
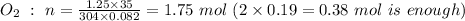
note: moles of CO₂ is the same as of CH₄, as can be seen from the chemical equation above, which is 0.19 mol.
Find volume of CO₂:
![\left[\begin{array}{ccccc}&Volume(L)&Pressure(atm)&Temperature(K)&Moles(mol)\\CO_(2) &?&2.5&398&0.19\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/14q5rhtpuh2un8dve7ccu03rhaexm4xqbz.png)
Formula to find Volume is:
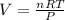
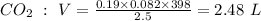
So, the answer is: 2.48 L