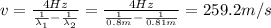The beat frequency (4 beat per second = 4 Hz ) corresponds to the difference between the frequencies of the two waves:
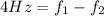
(1)
The frequency of the first wave can be written as
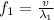
where v is the speed of sound in the gas and
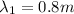
is the wavelength of the first wave, while the frequency of the second wave is
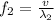
where
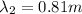
is the wavelength of the second wave. If we substitute into the first equation (1), we find
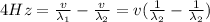
and if we re-arrange it, we can find the velocity of the sound in the gas: