Answer: C) decrease, increase, increasing.
Explanation: There is a depression in freezing point when a non volatile solute is added to the solvent and an elevation in boiling point when a non volatile solute is added to a solvent.
Pure water freezes at zero degree C. If a non volatile solute is added to water then solution freezes below zero degree C. On the other hands, if a non volatile solute is added to a solvent then boiling point increases.
The relationship between depression in freezing point and molality is shown by the equation:
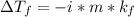
where,
 is depression in freezing point, i is Van't hoff factor, m is molality and kf is the molal freezing point depression constant.
is depression in freezing point, i is Van't hoff factor, m is molality and kf is the molal freezing point depression constant.
We have almost similar equation for elevation in boiling point.
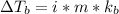
 stands for elevation in boiling point and kb stands for molal boiling point constant.
stands for elevation in boiling point and kb stands for molal boiling point constant.